Endodontics
.jpg)
Endodontic treatment (root canal treatment)
Pulp is a soft tissue filling the inside of the tooth located beneath hard tissues of the tooth (enamel and dentin). It consists of a web of nerves and blood vessels, soft connective tissue and various cells. If the pulp is damaged, the tooth becomes non-vital, because the blood vessels and nerves die, the tooth loses innervation – the connection to the central nervous system. Endodontic treatment is necessary when the pulp becomes infected. Microorganisms and their toxins enter pulp through small canals in the tooth from cavities, deep periodontal pockets, in case of trauma and other lesions (cracks, chips, erosions, non-carious cervical lesions, etc.).
Why do root canals need to be treated?
If the canals are not treated, the bacteria in the infected pulp can spread out of the root and cause inflammation of the surrounding tissues – periodontitis. The jaw bone starts to erode slowly. During the chronic phase of periodontitis the patient can experience no pain, although in case of flare-ups there can be severe pain and swelling. If the process continues, the tooth may have to be extracted.
Periodontitis of some upper teeth might cause sinusitis, the inflammation of the sinus mucosa.
Endodontic treatment increases the life of a tooth.
Signs and symptoms of pulp damage:
pain can be:
.jpg)
- persistent;
- acute, sharp, recurrent. Can radiate towards the ear. Usually manifests in evenings or at night.
- constant, sometimes numb, pulsing.
Pain can be provoked by:
- heat;
- biting or touching;
- no apparent reason;
- discoloration or the tooth;
- swelling gums, abscesses and sinus tracts;
- trauma. In case of trauma, you should see a dentist even if there is no visible damage to assess tooth vitality.
In some cases there are no symptoms. The need for root canal treatment can be determined only after clinical and radiological examination.
.jpg)
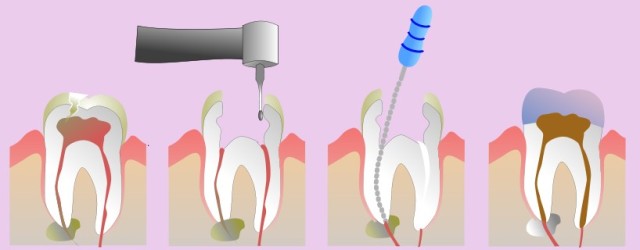
Root canal treatment procedure
First the dentist assesses tooth condition using various tests and X-rays. Clinicians at Neodenta use modern computer X-ray visiography systems reducing the exposure 4-10 times.
.jpg)
After anesthesia the tooth is isolated from saliva using a rubber dam, which also prevents endodontic instruments and dental materials from falling into the mouth.
The pulp chamber is opened. A cavity is prepared for easy access to root canals.
Treatment steps:
- mechanical and chemical treatment of canals to remove pulp;
- working length is determined using an apex locator; canals are cleaned and shaped using hand or rotary endodontic instruments. Mechanical cleaning does not remove the bacteria, so this method is combined with irrigation using chemical solutions. For a better effect the solutions are activated using ultrasound.
- canals are sealed using guttapercha, a sealing material.
In the clinic we fill canals:
- using guttapercha points and lateral condensation technique;
- using warm guttapercha (Calamus Maillefer) which fills the root canal system in three dimensions– not only the main canal, but also its lateral branches.
Although technologies advance and allow dentists to perform even complex procedures, it should be noted that there is a chance of treatment failure. Therefore it is recommended to cooperate with the dentist to follow up the tooth for at least 3-4 years.
.jpg)
What are the possible root canal treatment complications? Can it be necessary to repeat the treatment?
At Neodenta clinic root canal treatment is carried out using a operating microscope (Zeiss) which allows the clinician to see a greatly magnified and illuminated view. It dramatically reduces the possibility of failure.
At Neodenta clinic all possible root canal procedures are carried out
- primary root canal treatment
- root canal retreatment
- treatment of complicated curved canals
- treatment of calcified canals
- treatment of perforated canals
- treatment of resorbed canals
- extraction of foreign bodies (instruments, metal screws, silver posts, inlays)
- treatment of traumatized teeth
- diagnostics of root fractures
- treatment of not fully developed root canals