Surgical dentistry
Oral surgeons consult patients, treat inflammations of the jaw and periosteum and salivary glands, also cysts, granulomas, diseases of the temporomandibular joint, traumas to the jaws, inflammations of soft tissues (abscesses, lymphadenitis, etc.).
Tooth extraction is the most common surgical dental procedure.
Tooth extraction
It is a serious surgical procedure, so it is important to know that after extracting a tooth there is an individual healing period when dentist’s recommendations must be followed.
(1).jpg)
Common reasons for tooth extraction
- unerupted teeth;
- orthodontic reasons;
- purulent process around the root of the tooth;
- fracture of the tooth or the root;
- severe misalignment of the tooth;
- sever decay;
- advanced periodontal disease.
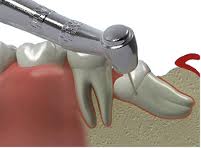
Wisdom teeth are exceptional not only because they erupt very late in life (usually in adulthood only), but also because they can cause many problems. They are hard to reach, their roots are often curved. Wisdom tooth extraction is a complicated surgical procedure.
Impacted or retained teeth are formed but unerupted teeth which do not perform chewing and so are recommended to be extracted. The surgery should be planned in advance due to varying healing period, it should be avoided before holidays, important meetings or weddings. It is reasonable to expect the face to be swollen for 3-5 days. Oral surgeon will evaluate your individual situation during the first visit.
Non-traumatic tooth extraction
The aim is to extract the tooth without damaging surrounding tissues, including the gums. The whole procedure (mobilization of the tooth, separation and removal of small fragments) is carried out using smaller instruments. The tooth socket is often closed. Non-traumatic tooth extraction is useful for implant or prosthetic treatment, especially in aesthetically important regions. The treated region heals quicker, there are dramatically less complications and discomfort for the patient.
Treatment of alveolitis
Alveolitis is inflammation caused by infection in the tooth socket (the space where the root used to be) when a blood clot doesn’t form or is lost.
Timely treatment is not difficult. There is medium severity pain, bad breath. After anesthesia bleeding is provoked to form a blood clot. If treatment is late, the disease becomes more severe. Treatment is also more difficult: the wound is irrigated, medicament dressing is inserted into the tooth socket and the patient has to come for visits every 2–3 days until the symptoms pass and the wound is covered by healing tissue.
(1).jpg)
Dental cyst
A cyst is a lesion around the tip of the root. All dental cysts are removed surgically. They are especially common for patients with impacted or retained teeth. If a tooth root is integrated into the cyst, its tip is removed and filled. The most common cause of dental cysts is non-vital pulp (the nerve of the tooth) and untreated root canals.
There are two types of dental cysts.
Inflammatory:
- radicular;
- paradental.
Developmental:
- folicular;
- lateral periodontal;
- keratocysts;
- glandular.
.jpg)
What should I do after having a tooth extracted?
Bite on the gauze the dentist has given for 30 minutes. It is there to absorb the blood and stop the bleeding.
- Do not eat for 2 hours.
- There might be some pain after the procedure. Take painkillers your dentist has prescribed.
It is recommended to eat only soft food the first 24 hours. Avoid hard, spicy or hot food that may cause pain and recurrent bleeding.
- On the same day DO NOT rinse the mouth with any mouthrinses.
- The next day gently rinse the mouth with mouthrinses.
- Do not touch the wound with your fingers or tongue.
- Brush teeth gently using a soft toothbrush avoiding the gums and the wound.
Look after the children while under anesthesia so as not to bide the cheeks. If anesthesia performed on the lower jaw, lay children on their side so the tongue does not cover the airways and the child does not choke.
- Take medicine as prescribed by your dentist.
- Avoid hard physical labor and drinking alcoholic beverages. Avoid hot environments.
- If you feel unwell, the bleeding or swelling is does not pass or you simply have questions, visit your dentist.






